Building a sustainable and eco-friendly modern lifestyle isn’t about drastic sacrifices; it’s about making conscious choices that benefit both you and the planet. It’s a journey of integrating environmentally friendly practices into your daily routine, from the food you eat to the way you commute. This exploration delves into practical strategies and innovative solutions to help you live a more sustainable life, reducing your environmental footprint while enhancing your well-being.
This guide covers various aspects of sustainable living, offering actionable steps to reduce your impact on the environment. We’ll explore practical home improvements, conscious consumption habits, sustainable transportation options, mindful food choices, and the role of community engagement in building a greener future. We also touch upon the exciting advancements in technology that are making sustainable living easier and more accessible than ever before.
Defining Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Living
Sustainable and eco-friendly living represents a conscious effort to minimize our environmental impact while fostering social equity and economic viability. It’s not about deprivation, but rather about making mindful choices that benefit both ourselves and future generations. This approach integrates environmental responsibility, social justice, and economic prudence into daily life, aiming for a harmonious relationship between humanity and the planet.Sustainable and eco-friendly living is guided by several key principles.
These principles work together to create a holistic approach to living in harmony with the environment and each other.
Key Principles of Sustainable Living
Adopting a sustainable lifestyle involves a conscious effort to adhere to several core principles. These principles are interconnected and contribute to a more balanced and environmentally responsible way of life. Understanding these principles is crucial for making informed choices that benefit both the individual and the planet.
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: This classic mantra emphasizes minimizing waste generation, maximizing the lifespan of products, and ensuring proper disposal of materials.
- Conserve Resources: This involves mindful use of water, energy, and other natural resources, aiming to minimize depletion and pollution.
- Support Local and Sustainable Businesses: Prioritizing locally sourced food and products reduces transportation emissions and supports ethical practices.
- Minimize Consumption: This involves questioning the need for new purchases and opting for experiences over material possessions. It also promotes mindful consumption, considering the environmental and social impact of products.
- Embrace Renewable Energy: Utilizing solar, wind, or other renewable energy sources reduces reliance on fossil fuels and their associated emissions.
Benefits of Sustainable Living for Individuals and Society
The benefits of adopting a sustainable lifestyle are numerous and extend to both individuals and society as a whole. These benefits range from improved personal well-being to a healthier planet for future generations.
- Improved Health and Well-being: A sustainable lifestyle often involves healthier dietary choices, increased physical activity (e.g., cycling instead of driving), and reduced exposure to harmful chemicals and pollutants, leading to improved physical and mental health.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Sustainable practices directly contribute to mitigating climate change, reducing pollution, and conserving natural resources for future generations. For example, reducing meat consumption can significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions associated with livestock farming.
- Cost Savings: While some initial investments may be required (e.g., in energy-efficient appliances), many sustainable practices, such as reducing energy consumption and water usage, can lead to significant long-term cost savings.
- Stronger Communities: Supporting local businesses and engaging in community initiatives fosters social connections and builds resilience within communities.
- Increased Awareness and Responsibility: Embracing a sustainable lifestyle promotes a deeper understanding of environmental issues and encourages responsible citizenship.
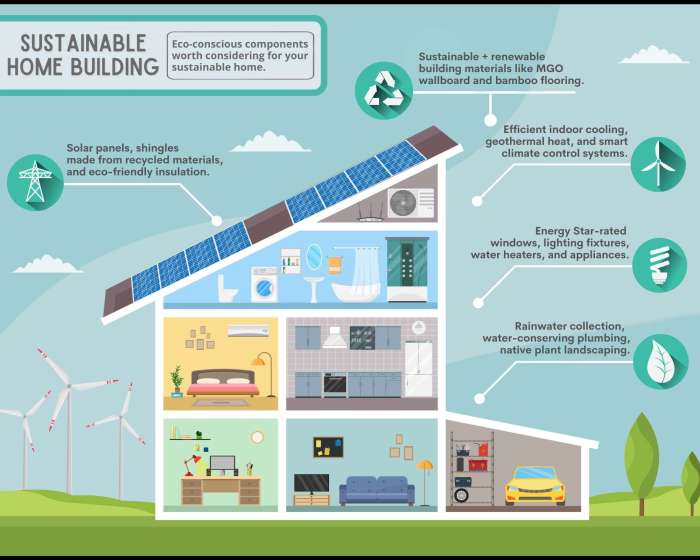
Sustainable Home Practices
Creating a sustainable home isn’t about drastic overhauls; it’s about making conscious choices that minimize environmental impact without sacrificing comfort. Small changes in design, appliance usage, and cleaning habits can collectively lead to significant reductions in your carbon footprint and resource consumption. This section explores practical strategies for building and maintaining an eco-friendly home.
Eco-Friendly Home Design and Energy Efficiency
Designing a sustainable home starts with considering passive solar design and energy-efficient features. Passive solar design maximizes natural sunlight for heating and minimizes energy needs for artificial lighting and heating. A well-designed home can significantly reduce reliance on energy-intensive systems. Consider a south-facing orientation (in the Northern Hemisphere) to capture maximum sunlight during winter. Large windows facing south allow for passive solar heating, while overhangs or awnings can shade windows during summer, reducing cooling needs.
Proper insulation in walls, roofs, and floors minimizes heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Using materials with high thermal mass, such as concrete or brick, helps regulate indoor temperatures.Here’s a sample floor plan incorporating these principles:Imagine a two-story home with a south-facing living room and kitchen. Large windows in the living room allow for abundant natural light and passive solar heating.
The kitchen is positioned to take advantage of the morning sun. Bedrooms are located on the second floor, away from the heat-generating areas. The roof is designed with high insulation and incorporates solar panels for renewable energy generation. The overall design emphasizes natural ventilation, minimizing the need for air conditioning.
Energy Consumption of Home Appliances
Understanding the energy consumption of different appliances is crucial for reducing household energy use. The following table compares the typical annual energy consumption of common household appliances:
| Appliance | Average Annual Energy Consumption (kWh) |
|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 1500-2000 |
| Washing Machine | 500-1000 |
| Dryer | 1000-2000 |
| Dishwasher | 300-500 |
| Television | 100-200 |
Note: These are average values and actual consumption can vary depending on usage, model, and energy efficiency rating. Look for appliances with high Energy Star ratings for greater energy efficiency.
Reducing Household Water and Energy Consumption
Conserving water and energy are intertwined aspects of sustainable living. Simple changes can significantly reduce both.
- Install low-flow showerheads and faucets to reduce water usage without compromising water pressure.
- Fix leaky faucets and toilets promptly to prevent water waste. A dripping faucet can waste gallons of water over time.
- Run full loads in your washing machine and dishwasher to optimize energy and water efficiency.
- Air-dry clothes whenever possible instead of using a dryer. This saves significant energy and reduces wear and tear on clothing.
- Use energy-efficient LED lighting throughout your home. LEDs use significantly less energy than incandescent or CFL bulbs.
- Unplug electronics and appliances when not in use to prevent “phantom load,” which is the energy consumed by devices even when turned off.
Eco-Friendly Cleaning Products
Choosing eco-friendly cleaning products minimizes exposure to harsh chemicals and reduces environmental impact. Many effective cleaning solutions can be made from natural ingredients.
- Baking Soda: A versatile cleaner for scrubbing, deodorizing, and scouring. Use it to clean countertops, sinks, and ovens.
- White Vinegar: Effective for cleaning windows, mirrors, and removing hard water stains. It’s also a natural disinfectant.
- Lemon Juice: A natural bleaching and deodorizing agent, useful for cleaning cutting boards and removing stains.
- Castile Soap: A plant-based soap that can be diluted with water to create a multi-purpose cleaner for floors, surfaces, and dishes.
- Essential Oils (e.g., tea tree, lavender): Add a few drops to your cleaning solutions for a pleasant scent and added disinfectant properties.
Conscious Consumption and Waste Reduction
Embracing a sustainable lifestyle necessitates a conscious shift in our consumption habits and a determined effort to minimize waste. This involves actively reducing our reliance on single-use items, embracing reuse and recycling, and critically evaluating our purchasing decisions. By making mindful choices, we can significantly lessen our environmental footprint and contribute to a healthier planet.
A comprehensive waste reduction plan requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing recycling, composting, and a conscious reduction in overall consumption. This involves understanding the lifecycle of our waste and making informed decisions at every stage, from purchasing to disposal. Let’s examine effective strategies in more detail.
Waste Reduction Strategies
The following table Artikels various waste types, their appropriate disposal methods, and effective strategies for minimizing their generation.
| Waste Type | Disposal Method | Reduction Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Paper (newspapers, cardboard, etc.) | Recycling | Reduce paper consumption by opting for digital bills and statements. Choose products with minimal packaging. Buy recycled paper products. |
| Plastics (bottles, containers, packaging) | Recycling (where available), proper disposal | Reduce plastic consumption by choosing products with minimal or recyclable plastic packaging. Opt for reusable alternatives like water bottles and shopping bags. Support businesses that prioritize sustainable packaging. |
| Glass (bottles, jars) | Recycling | Buy products in glass containers whenever possible. Support businesses that utilize refillable glass containers. |
| Food Scraps | Composting | Plan meals to reduce food waste. Store food properly to extend its shelf life. Compost food scraps to enrich soil and reduce landfill waste. |
| Textiles (clothing, towels) | Donation, recycling (specific programs), proper disposal | Buy high-quality, durable clothing items. Repair and mend clothing instead of discarding it. Support clothing brands committed to sustainable practices. |
| Electronics (computers, phones) | E-waste recycling programs | Extend the life of electronics through repair and maintenance. Choose durable, repairable electronics. Participate in responsible e-waste recycling programs. |
The Environmental Impact of Fast Fashion and Sustainable Alternatives
Fast fashion, characterized by the rapid production of trendy, low-cost clothing, has a devastating environmental impact. The industry contributes significantly to water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and textile waste. The use of synthetic fabrics, often derived from petroleum, further exacerbates these issues. Moreover, the low quality of fast fashion garments often leads to short lifespans and increased consumption.
Sustainable alternatives involve prioritizing quality over quantity, choosing durable, ethically produced clothing, and supporting brands committed to sustainable practices. This includes opting for natural fabrics like organic cotton, linen, and hemp, and supporting clothing rental services or secondhand clothing markets. Investing in timeless pieces that can be worn for years, rather than fleeting trends, is also crucial. Repairing and repurposing existing clothing items extends their lifespan and reduces waste.
Sustainable Packaging Options
The packaging industry is a significant contributor to waste. However, there are many sustainable alternatives emerging. A comparison of some common options follows:
Paper-based packaging: Recyclable and biodegradable, but can require significant tree harvesting if not sourced sustainably. Often requires additional coatings or treatments to improve its performance.
Bioplastics: Made from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, offering biodegradability. However, their environmental impact depends heavily on the production process and disposal methods. Not all bioplastics are compostable in home composting systems.
Glass: Infinitely recyclable and inert, making it a very sustainable option. However, it is heavy and prone to breakage, resulting in transportation challenges and potential for injury.
Reusable containers: Represent a significant reduction in waste by eliminating single-use packaging altogether. Requires a shift in consumer behavior and infrastructure to support refilling systems.
The most sustainable packaging option often depends on the specific product and its lifecycle. A holistic approach, considering factors like material sourcing, manufacturing process, and end-of-life management, is essential for making informed choices.
Sustainable Transportation and Mobility
Adopting sustainable transportation is crucial for reducing our carbon footprint and improving air quality. By shifting away from reliance on private vehicles, we can create healthier, more livable cities and contribute to a more environmentally responsible future. This section explores various eco-friendly transportation options and strategies for promoting sustainable commuting habits.
Comparison of Eco-Friendly Transportation Options
Choosing sustainable transportation involves considering several factors, including cost, convenience, and environmental impact. The following table compares some popular options:
| Transportation Mode | Environmental Impact | Cost | Convenience | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycling | Very Low | Low (initial bike purchase) | Moderate (dependent on distance and terrain) | Moderate (dependent on infrastructure) |
| Public Transport (Bus, Train, Subway) | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High (depending on frequency of use and location) | Moderate to High (dependent on route availability and frequency) | High (in urban areas with well-developed public transit systems) |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Low (depending on electricity source) | High (initial purchase price, but potentially lower running costs) | High (similar convenience to petrol cars) | Moderate (dependent on charging infrastructure availability) |
| Carpooling | Moderate (reduced emissions per person compared to individual car use) | Moderate (shared fuel costs) | Moderate (dependent on scheduling and coordination with other passengers) | Moderate (dependent on availability of carpool partners) |
Strategies for Reducing Reliance on Personal Vehicles
Minimizing our reliance on personal vehicles requires a multi-pronged approach. This includes promoting alternative transportation modes, improving public transit systems, and implementing policies that incentivize sustainable commuting.Several effective strategies include:* Investing in cycling infrastructure: Creating dedicated bike lanes, secure bike storage facilities, and improving road safety for cyclists encourages more people to choose cycling as a primary mode of transport.
Examples of successful implementations can be seen in cities like Amsterdam and Copenhagen, where extensive cycling networks have significantly reduced car dependency.* Improving public transportation: This involves increasing the frequency and reliability of bus, train, and subway services, expanding routes to cover a wider area, and improving accessibility for people with disabilities. Cities like London and Tokyo serve as examples of effective and extensive public transportation networks.* Implementing incentives for sustainable commuting: Governments can incentivize the use of public transport, cycling, and walking through measures such as tax breaks, subsidies for public transport passes, and dedicated parking for bicycles and electric vehicles.
Examples include offering discounted fares for public transport users during off-peak hours or providing financial incentives for purchasing electric bicycles.* Promoting carpooling and ride-sharing: Encouraging carpooling through dedicated apps and platforms, along with incentives for employers to facilitate carpools, can significantly reduce the number of cars on the road. Companies like Waze and BlaBlaCar are examples of ride-sharing platforms that are contributing to this effort.
The Role of Urban Planning in Promoting Sustainable Transportation
Urban planning plays a vital role in shaping transportation choices. Well-planned cities prioritize pedestrian and cyclist safety, provide efficient public transportation networks, and minimize the need for private vehicles.Key aspects of urban planning that promote sustainable transportation include:* Mixed-use zoning: Designing neighborhoods with a mix of residential, commercial, and recreational areas reduces the need for long commutes by car.
This allows residents to access essential services and amenities within walking or cycling distance.* Transit-oriented development: Developing high-density housing and commercial areas around public transportation hubs encourages the use of public transport. This minimizes reliance on private vehicles and reduces traffic congestion.* Pedestrian and cyclist-friendly infrastructure: Creating safe and convenient walking and cycling paths, including dedicated bike lanes, pedestrian crossings, and well-lit streets, encourages people to choose active modes of transport.* Reducing reliance on private vehicles through parking restrictions and pricing: Implementing policies like congestion charges and limited parking spaces in city centers can discourage car use and promote alternative modes of transportation.
Examples include London’s congestion charge zone and similar initiatives in other major cities worldwide.
Sustainable Food Choices and Diet
Source: ambientbp.com
Adopting a sustainable diet is a crucial step towards a greener lifestyle. It involves making conscious choices about the food we consume, considering its environmental impact from farm to table. By prioritizing plant-based foods, locally sourced ingredients, and seasonal produce, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and support more sustainable agricultural practices.Choosing sustainable food sources minimizes the environmental burden associated with food production, transportation, and waste.
This approach not only benefits the planet but also contributes to a healthier and more ethical food system.
Building a sustainable and eco-friendly modern lifestyle isn’t about sacrificing luxury; it’s about redefining it. For entrepreneurs seeking to build a brand that reflects their values, consider the impact of conscious consumption. Check out this guide on Creating a luxury lifestyle brand for entrepreneurs to learn how to integrate sustainability into your business model and create a truly luxurious, eco-conscious brand.
This approach allows you to enjoy a high-quality life while minimizing your environmental footprint.
A Sample Weekly Plant-Based Meal Plan Emphasizing Local and Seasonal Foods
This sample meal plan focuses on readily available ingredients and can be adjusted based on your location and seasonal produce. Remember to check your local farmers’ markets for the freshest, most sustainable options.
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Oatmeal with berries and nuts | Lentil soup with whole-grain bread | Roasted vegetables (seasonal) with quinoa |
| Tuesday | Smoothie with spinach, banana, and almond milk | Salad with chickpeas, avocado, and a lemon vinaigrette | Vegetable curry with brown rice |
| Wednesday | Tofu scramble with vegetables | Leftover vegetable curry | Pasta with pesto and cherry tomatoes |
| Thursday | Yogurt with fruit and granola | Black bean soup with cornbread | Lentil Shepherd’s Pie with sweet potato topping |
| Friday | Breakfast burrito with black beans and vegetables | Salad with grilled halloumi (optional, for non-vegan) | Pizza with seasonal vegetables |
| Saturday | Pancakes made with whole-wheat flour | Leftover pizza | Vegetable stir-fry with noodles |
| Sunday | French toast with berries | Soup with whole-grain bread | Roasted chicken (optional, for non-vegan) with roasted root vegetables |
Environmental Impacts of Different Food Production Methods
Different food production methods have vastly different environmental impacts. Industrial agriculture, characterized by large-scale monoculture farming and intensive use of pesticides and fertilizers, contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, soil degradation, water pollution, and biodiversity loss. In contrast, sustainable agriculture practices, such as agroforestry, permaculture, and organic farming, aim to minimize these negative impacts by prioritizing soil health, biodiversity, and reduced reliance on synthetic inputs.
For example, a study by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) highlighted the significant contribution of livestock farming to greenhouse gas emissions, emphasizing the environmental benefits of reducing meat consumption.
Benefits of Reducing Meat Consumption and Adopting a Plant-Based Diet
Reducing meat consumption and adopting a more plant-based diet offers numerous environmental benefits. Animal agriculture is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. Plant-based diets generally have a much smaller carbon footprint, require less land and water, and contribute less to pollution. Moreover, a shift towards plant-based eating can improve personal health by reducing the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
For instance, the EAT-Lancet Commission report proposed a dietary shift towards more plant-based foods as a key strategy for achieving sustainable food systems.
Sustainable Energy and Resource Management

Source: googleapis.com
Embracing sustainable energy and resource management is crucial for building a truly eco-friendly lifestyle. It involves making conscious choices to minimize our environmental impact through both behavioral changes and the adoption of innovative technologies. By reducing our reliance on non-renewable resources and embracing renewable alternatives, we can significantly contribute to a healthier planet for future generations.Reducing energy consumption is a key aspect of sustainable living, achievable through a combination of mindful practices and technological upgrades.
This includes both our homes and our workplaces, where significant energy savings can be realized.
Reducing Energy Consumption at Home and Work
Implementing energy-efficient practices at home and in the workplace can significantly reduce our carbon footprint. Simple behavioral changes, coupled with smart technology, can lead to substantial savings.
Building a sustainable and eco-friendly modern lifestyle isn’t about deprivation; it’s about conscious choices. It’s about redefining luxury, which is perfectly illustrated by this article on Building a sustainable luxury lifestyle for future generations. Ultimately, a sustainable future means embracing responsible consumption and creating a better world, both for ourselves and those who follow.
- Switching to LED lighting: LED bulbs consume significantly less energy than incandescent or even CFL bulbs, resulting in lower electricity bills and a smaller carbon footprint. For example, replacing a 60-watt incandescent bulb with a 10-watt LED bulb results in an 83% reduction in energy consumption.
- Unplugging electronics: Many electronic devices continue to draw power even when turned off (“phantom load”). Unplugging chargers, TVs, and other appliances when not in use can noticeably reduce energy consumption.
- Improving insulation: Proper insulation in walls, roofs, and windows minimizes heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems. This can lead to significant energy savings, often exceeding 20% depending on the existing insulation levels and climate.
- Using energy-efficient appliances: Look for appliances with high energy-efficiency ratings (e.g., Energy Star certified) when making purchases. These appliances are designed to consume less energy while maintaining performance.
- Adopting smart home technology: Smart thermostats and power strips allow for automated control of energy usage, optimizing heating, cooling, and appliance operation based on occupancy and usage patterns. For instance, a smart thermostat can learn your preferences and adjust the temperature accordingly, saving energy while maintaining comfort.
The Importance of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal, offer a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing our reliance on finite resources and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. These sources are naturally replenished and produce minimal or no pollution.
- Solar power: Harnessing sunlight to generate electricity through photovoltaic cells is a clean and increasingly cost-effective way to power homes and businesses. Residential solar panels can significantly reduce or even eliminate reliance on the grid, resulting in substantial long-term cost savings and reduced carbon emissions. Large-scale solar farms contribute to the generation of renewable energy on a wider scale.
- Wind power: Wind turbines convert wind energy into electricity. Wind farms, often located in areas with consistent strong winds, can provide a significant source of clean energy. The technology has advanced significantly, leading to larger, more efficient turbines that generate more electricity with less environmental impact.
- Hydropower: Utilizing the energy of flowing water to generate electricity through dams and turbines is a mature renewable energy technology. While large-scale hydropower projects can have environmental impacts, smaller-scale hydro projects can be more sustainable and provide localized renewable energy.
Conserving Water Resources
Water conservation is vital for ensuring the long-term availability of this precious resource. Implementing water-saving practices at home and promoting responsible water management in the community are crucial steps toward sustainability.
- Installing low-flow showerheads and faucets: These fixtures significantly reduce water consumption without compromising water pressure. Switching to low-flow fixtures can lead to considerable savings in both water and energy used for heating water.
- Fixing leaks promptly: A seemingly small leak can waste a surprising amount of water over time. Regularly checking for and repairing leaks can significantly reduce water waste.
- Using water-efficient appliances: Choosing water-efficient washing machines and dishwashers can substantially reduce water usage during these household chores. Many newer models feature advanced water-saving technologies.
- Collecting rainwater: Rainwater harvesting systems can collect rainwater for use in gardening, cleaning, and even toilet flushing, reducing reliance on municipal water supplies.
- Promoting community-level water conservation: Supporting initiatives that promote responsible water management, such as water recycling programs and public awareness campaigns, contributes to the collective effort of conserving water resources.
Community Engagement and Collective Action: Building A Sustainable And Eco-friendly Modern Lifestyle
Building a truly sustainable future requires more than individual efforts; it necessitates collective action and community engagement. By working together, we can amplify our impact and create lasting positive change for the environment. This involves actively participating in local initiatives, advocating for sustainable policies, and educating others about the importance of eco-friendly practices.Community initiatives play a crucial role in fostering sustainable living.
They provide platforms for collaboration, resource sharing, and collective problem-solving. The combined efforts of individuals within a community can lead to significant environmental improvements.
Examples of Community Initiatives Promoting Sustainable Living
Many communities are actively involved in promoting sustainable practices. For example, community gardens provide fresh, locally sourced produce, reducing reliance on energy-intensive industrial agriculture and transportation. These gardens also often serve as educational spaces, teaching residents about sustainable gardening techniques. Another example is the rise of community composting programs, where residents collectively compost organic waste, diverting it from landfills and creating valuable soil amendment.
Repair cafes, where volunteers help residents repair broken items instead of discarding them, exemplify the shift towards a circular economy, reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency. Finally, initiatives like neighborhood cleanup days and citizen science projects (e.g., monitoring local water quality) encourage direct community involvement in environmental stewardship.
The Role of Education and Awareness Campaigns in Fostering Sustainable Practices
Education and awareness campaigns are vital for driving the adoption of sustainable practices. These campaigns aim to inform the public about environmental challenges, the benefits of sustainable living, and practical steps individuals can take to make a difference. Effective campaigns use various methods, including public service announcements, educational workshops, and interactive online resources, to reach diverse audiences and encourage participation.
For example, a successful campaign might highlight the impact of individual choices on climate change, providing concrete examples of how reducing energy consumption, choosing sustainable transportation, or adopting a plant-based diet can contribute to a greener future. The ultimate goal is to empower individuals with the knowledge and motivation to make informed, sustainable choices.
Ways Individuals Can Participate in Collective Action to Promote Environmental Sustainability
Individuals can contribute to collective action in various ways. Participating in local environmental organizations, attending community meetings focused on sustainability, and advocating for environmentally friendly policies are all effective strategies. Signing petitions, contacting elected officials to express support for sustainable initiatives, and volunteering for environmental cleanup projects demonstrate a commitment to collective action. Furthermore, supporting businesses and organizations that prioritize sustainability through conscious consumption choices reinforces the demand for eco-friendly products and services.
Finally, sharing knowledge and inspiring others to adopt sustainable practices through conversations, social media, and community events can significantly amplify the impact of individual efforts.
Technological Advancements for Sustainable Living
Technology plays an increasingly vital role in creating a more sustainable future. From optimizing energy consumption in our homes to revolutionizing transportation and agriculture, innovative solutions are constantly emerging to lessen our environmental footprint and improve resource management. These advancements offer promising pathways towards a greener and more equitable world, but their ethical implications must be carefully considered.Technological solutions are actively reshaping various sectors, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in sustainable living.
This includes significant progress in renewable energy generation, smart agriculture, and waste management. The potential for positive impact is immense, but challenges remain in ensuring equitable access and responsible development.
Smart Home Systems and Energy Efficiency
Smart home technology offers a powerful toolkit for reducing energy consumption. Smart thermostats, for example, learn user preferences and adjust temperatures accordingly, minimizing energy waste. Similarly, smart lighting systems use sensors to automatically switch lights on and off, while smart appliances optimize energy usage based on real-time demand. The cumulative effect of these technologies can lead to significant reductions in household energy bills and carbon emissions.
For instance, a study by the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory found that smart thermostats can reduce energy consumption by 10-15% on average. This translates to considerable savings for homeowners and a collective decrease in greenhouse gas emissions.
Building a sustainable and eco-friendly modern lifestyle isn’t just about saving the planet; it’s about smart long-term planning. Investing wisely now ensures a comfortable future, and securing a luxurious retirement is a key part of that. Check out this guide on Best ways to invest for a luxury lifestyle retirement to help plan your financial future, allowing you to enjoy a sustainable and fulfilling retirement, all while minimizing your environmental impact.
Water Purification Technologies
Access to clean drinking water is a global challenge. Innovative water purification technologies are crucial for addressing water scarcity and improving public health. Reverse osmosis, ultraviolet disinfection, and nanofiltration are among the methods used to remove contaminants from water sources, making them safe for consumption. These technologies are particularly impactful in regions with limited access to clean water, contributing to improved sanitation and reduced waterborne diseases.
Furthermore, advancements in water harvesting and greywater recycling systems are enabling more efficient water management in both urban and rural settings. For example, the use of rainwater harvesting systems in arid regions reduces reliance on dwindling groundwater supplies and helps conserve precious water resources.
Building a sustainable and eco-friendly modern lifestyle often involves mindful consumption and reduced reliance on traditional employment. This can be achieved by generating alternative income streams, such as exploring the options detailed in this helpful article on Securing a luxury lifestyle through passive income streams. Ultimately, financial freedom allows for greater investment in sustainable practices, closing the loop and enabling a more environmentally conscious life.
Sustainable Transportation Technologies
The transportation sector is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid vehicles, and advancements in public transportation systems are crucial for reducing this impact. The development of more efficient batteries and charging infrastructure is essential for widespread EV adoption. Furthermore, autonomous vehicles have the potential to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion, leading to lower fuel consumption and emissions.
The expansion of high-speed rail networks and the integration of cycling and walking infrastructure can further reduce reliance on private vehicles. For example, cities like Amsterdam have significantly reduced their carbon footprint through extensive investments in cycling infrastructure and public transportation.
Ethical Considerations in Sustainable Technology, Building a sustainable and eco-friendly modern lifestyle
The development and deployment of sustainable technologies are not without ethical considerations. Ensuring equitable access to these technologies is crucial, as their benefits should not be limited to wealthy individuals or nations. The environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of these technologies must also be carefully assessed, minimizing the creation of electronic waste. Furthermore, the potential for data privacy concerns associated with smart home systems and other connected devices needs to be addressed.
Transparency and accountability are key to ensuring that sustainable technologies are developed and used responsibly, contributing to a truly sustainable and equitable future.
Closing Notes
Embracing a sustainable and eco-friendly modern lifestyle is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for a healthier planet and a more fulfilling life. By implementing the strategies discussed—from minimizing waste and choosing sustainable transportation to supporting local farmers and adopting energy-efficient practices—we can collectively create a positive impact. Remember, every small change contributes to a larger, more sustainable future.
Let’s build a world where environmental responsibility and modern convenience coexist harmoniously.
Clarifying Questions
What’s the difference between sustainable and eco-friendly?
While often used interchangeably, “eco-friendly” focuses primarily on environmental impact, while “sustainable” encompasses environmental, social, and economic considerations for long-term well-being.
How can I afford a sustainable lifestyle?
Sustainability doesn’t have to be expensive. Start with small, affordable changes like reducing energy consumption, reusing items, and buying less. Prioritize durable, high-quality items over cheap, disposable ones.
Is it realistic to be completely sustainable?
Complete sustainability is a challenging goal. The key is to strive for continuous improvement and make conscious choices to minimize your impact as much as possible. Every effort counts.
What if I live in an apartment and can’t make major home renovations?
Even in apartments, you can make a difference through energy-saving habits, mindful consumption, and recycling. Focus on what you
-can* control within your living space.
Where can I find more information and resources?
Numerous online resources, local environmental organizations, and government websites offer valuable information and support for sustainable living.